Getting started with Terraform
Infrastructure as a Code.
What Devops brings to the table?
Understand the application functional requirements: What must do?
Analyze and deduce non-functional requirements: How should do?
Design | Architect: How well architected it should be?
Build | Test | Deploy: How to ship fast and frequently?
Communication - Bringing development & operations activities together.
The Five Pillars of the Devops
Operational Excellence
How support development and run workloads effectively ?
Security
How to secure infrastructure, application and data ?
Reliability
How to perform application intended function correctly & consistently when it’s expected to ?
Performance
How to use computing resources efficiently to meet system requirements ?
Cost
How to run systems to deliver business value at the lowest price point?
Link: https://wa.aws.amazon.com/wellarchitected/2020-07-02T19-33-23/wat.pillars.wa-pillars.en.html
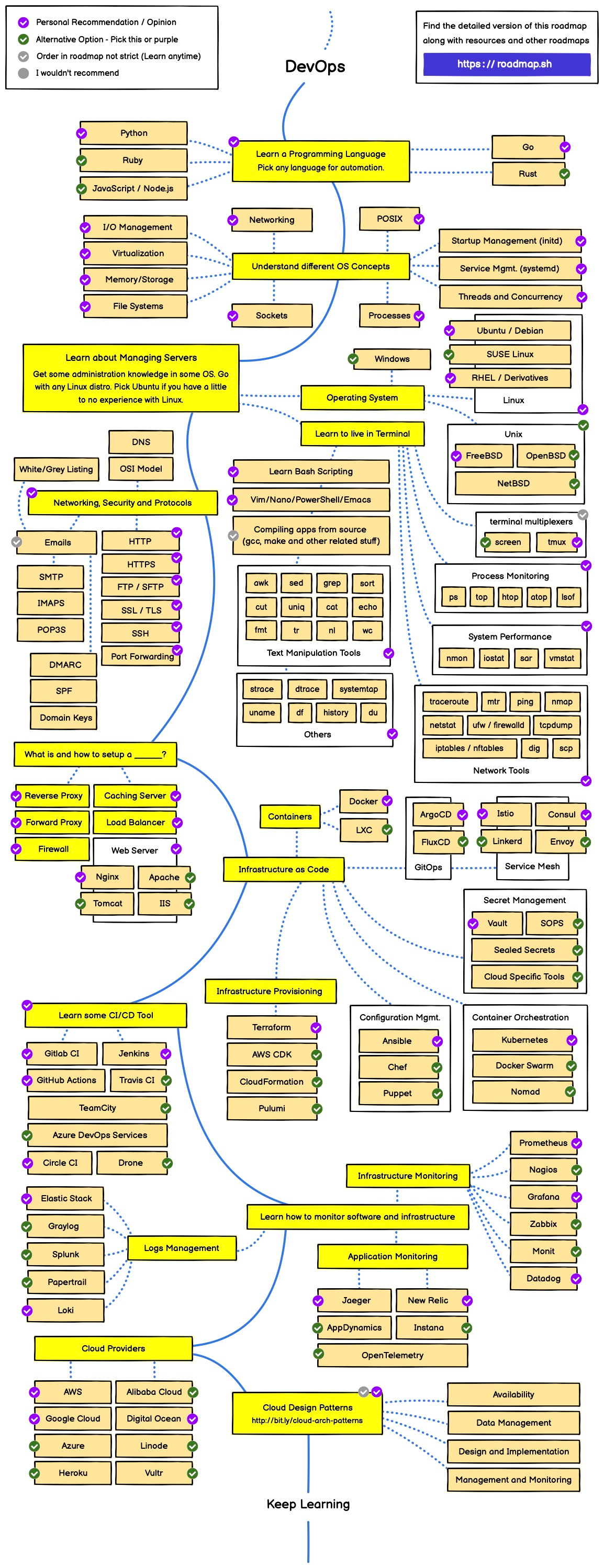
Devops Roadmap
Programming: Python, Shell etc.
System | Network: Unix, OSI model, Protocols
Cloud Providers: AWS, GCP, Azure
Build | Release | Testing: Github, Argo etc.
Infrastructure: Terraform (IAC), Helm, Kubernetes etc.
Security: Confidentiality | Integrity | Availability
Operate: Log | Monitoring | Configuration Management
Link: https://roadmap.sh/devops
Terraform Development Workflow
Terraform is an open-source infrastructure as code software tool that enables you to safely and predictably create, change, and improve infrastructure.
Link: https://github.com/hashicorp/terraform
Challenges
Repetitive works for environments, error prone to typos, mistakes
Terraform tooling increase, number of manual steps go up
Debugging becomes challenging, more modules, nested modules, environments
Visualization and dependency tracking becomes hard
What workspaces calls what modules?
What workspace resources are in-use?
Onboarding tooling, best practices wrap up time increases
PR Reviews require more time and back and forth discussions
Modules, providers upgrade & maintenance tracking and time increase
Continuous Refactoring becomes harder with lack of full picture ( change blast radius)
Versioning
Terraform version manager tfenv:
brew install tfenvTesting
1. Functional
It provides a variety of helper functions and patterns for common infrastructure testing tasks:
Link: https://github.com/gruntwork-io/terratest
2. Security
Negative testing versus functional testing:
Negative testing is a method of testing an application or system that ensures that the plot of the application is according to the requirements and can handle the unwanted input and user behavior.
Terrascan is a static code analyzer for Infrastructure as Code.
$ tfsec .$ terrascan scan .Link: https://github.com/terraform-compliance/cli
Link: https://github.com/accurics/terrascan
3. Syntax check
Validates the configuration files:
terraform validate -json
{
"format_version": "0.1",
"valid": true,
"error_count": 0,
"warning_count": 0,
"diagnostics": []
}
4. Linting
TFLint is a framework and each feature is provided by plugins, the key features are as follows:
Find possible errors (like illegal instance types) for Major Cloud providers (AWS/Azure/GCP).
Warn about deprecated syntax, unused declarations.
Enforce best practices, naming conventions.
brew install tflint
terraform fmt -recursive
5. Tagging
Terratag is a CLI tool allowing for tags or labels to be applied across an entire set of Terraform files. Terratag will apply tags or labels to any AWS, GCP and Azure resources:
brew install env0/terratag/terratag
terratag -tags={\\"env0_environment_id\\":\\"dev\\",\\"env0_project_id\\":\\"clientA\\"}
Link: https://github.com/env0/terratag
6. Self-documenting code
terraform-docs markdown table --footer-from footer.md ./examples/
Logging & Debugging
Set
TF_LOGto one of the log levels to change the verbosity of the logs.TRACE
DEBUG
INFO
WARN
ERROR
Logging can be enabled separately for terraform itself and the provider plugins:
TF_LOG_CORETF_LOG_PROVIDER
Set
TF_LOG_PATHto persist logged outputSet playbook it per module
If terraform is able login?
If workspace settings are as expected?
At what stage terraform fails and what error message says?
Is error coming from module?
If all required variables passed to module?
Local development workflow
Go to environment workspace
Initialize terraform to pull modules from Terraform Cloud registry if needed.
If require module changes:
Find module github repo and pull
After changes made push to new branch in git
From environment workspace point to branch
Merge branch to main
Publish new release
Point from environment workspace to new release of module
Best practices
Naming Conventions
Resource names
Variable names
Output names
Module names
Tag names
Hashicorp maintained: https://developer.hashicorp.com/terraform/cloud-docs/recommended-practices
Google maintained: https://cloud.google.com/docs/terraform/best-practices-for-terraform
Community maintained: https://www.terraform-best-practices.com
Community maintained for AWS: https://github.com/ozbillwang/terraform-best-practices
A weekly newsletter about Terraform ecosystem: https://weekly.tf